1:100 – Optimizing the supply and trading of positions in international markets. Discover all the products and services that Trade master has to offer.
Oil trading is the buying and selling of different types of oil and oil-linked assets with the aim of making a profit. As oil is a finite resource, its price can see massive fluctuations due to supply and demand changes. This volatility makes it extremely popular among traders.
You can use CFDs to trade on oil’s spot price, or the prices of oil futures or options contracts, without having to own any actual oil.
There are three ways you can trade oil:
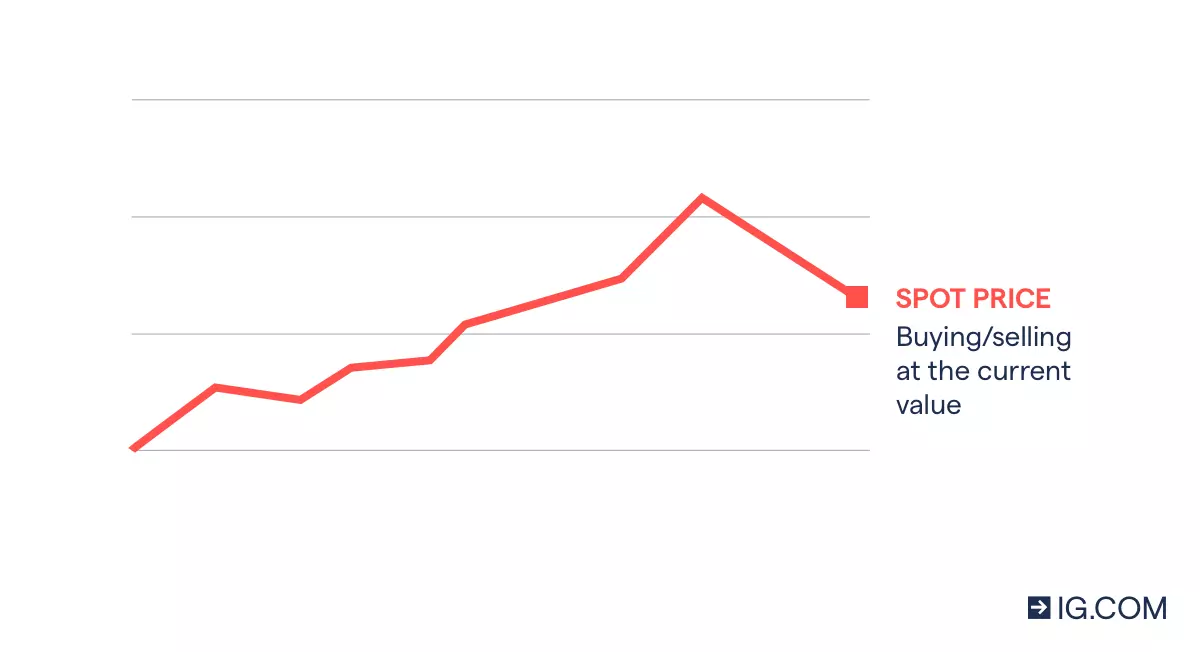
1. What is the oil spot price?
Oil spot prices represent the cost of buying or selling oil immediately, or ‘on the spot’ – instead of at a set date in the future. While futures prices reflect how much the markets believe oil will be worth when the future expires, spot prices show how much it is worth right now.
2. What are oil futures?
Oil futures are contracts in which you agree to exchange an amount of oil at a set price on a set date. They’re traded on exchanges and reflect the demand for different types of oil. Oil futures are a common method of buying and selling oil, and they enable you to trade rising and falling prices.
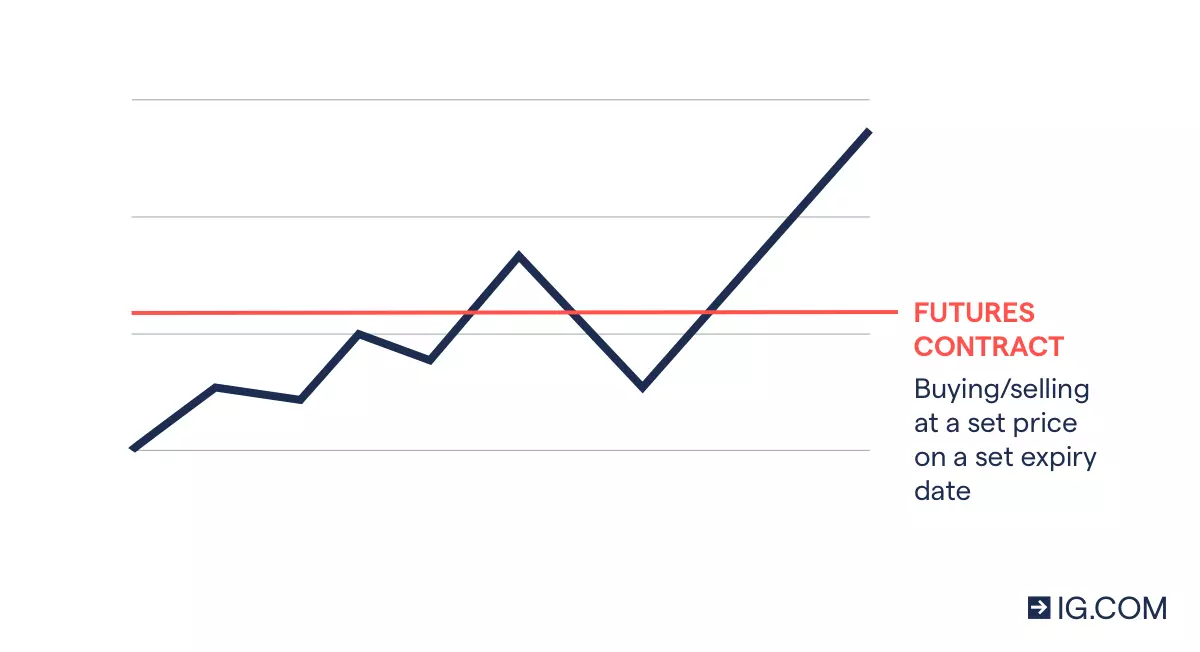
Futures are used by companies to lock in an advantageous price for oil and hedge against adverse price movements. However, they’re popular among speculative traders too as there is no need to take delivery of barrels of oil – although you have to fulfil the contract, this can be via a cash settlement.
The two most popular types are Brent Crude and West Texas Intermediate (WTI), which are traded on the Intercontinental Exchange (ICE) and New York Mercantile Exchange (NYMEX) respectively. They are used as benchmarks for global oil prices, as well as economic health.

